These commands cover a wide range of tasks and are essential for managing files, processes, users, networks, and system configurations in a Linux environment.

- ls: List directory contents.
- cd: Change the current directory.
- pwd: Print the name of the current directory.
- mkdir: Create a new directory.
- rm: Remove files or directories.
- cp: Copy files or directories.
- mv: Move or rename files or directories.
- cat: Concatenate and display file content.
- less: Display file content one page at a time.
- head: Display the beginning of a file.
- tail: Display the end of a file.
- grep: Search for patterns in files.
- chmod: Change file permissions.
- chown: Change file ownership.
- sudo: Execute a command with superuser privileges.
- su: Switch to another user account.
- df: Display disk space usage.
- du: Display disk usage for files and directories.
- find: Search for files and directories.
- locate: Find files by name.
- tar: Archive files.
- gzip: Compress or decompress files.
- zip: Package and compress files.
- unzip: Extract files from a ZIP archive.
- ssh: Connect to a remote server securely.
- scp: Securely copy files between hosts.
- wget: Download files from the web.
- curl: Transfer data from or to a server.
- ps: Display information about running processes.
- kill: Terminate processes.
- top: Display real-time system information.
- uptime: Display system uptime.
- uname: Print system information.
- ifconfig: Display network interface configuration.
- ping: Test network connectivity.
- traceroute: Trace the route to a remote host.
- netstat: Display network connections, routing tables, and interface statistics.
- iwconfig: Configure wireless network interfaces.
- iptables: Configure firewall rules.
- route: View and manipulate the IP routing table.
- adduser: Create a new user account.
- usermod: Modify user account properties.
- passwd: Change user password.
- groupadd: Create a new group.
- groups: Display group membership for a user.
- w: Display who is logged in and what they are doing.
- last: Display a list of last logged-in users.
- history: Display command history.
- date: Display or set the system date and time.
- cal: Display a calendar.
ls: List directory contents
cd: Change the current directory

pwd: Print the name of the current directory

mkdir: Create a new directory
rm: Remove files or directories
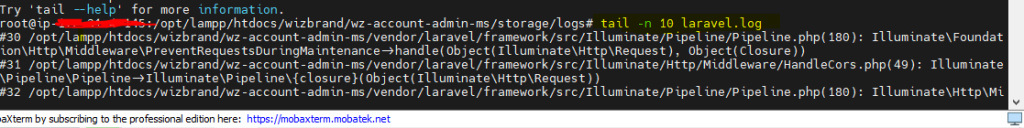
tail: Display the End of a File
man – Manual Pages
The man command is used to display the manual pages of other commands

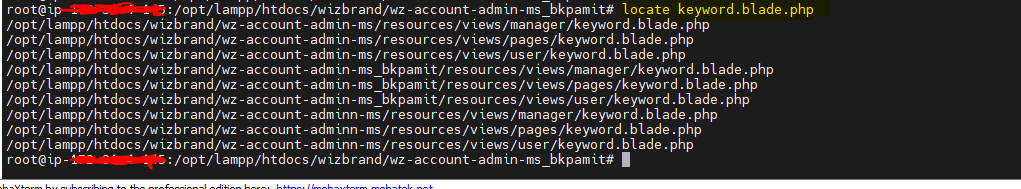
locate: Find files by name
sudo: Execute a command with superuser privileges

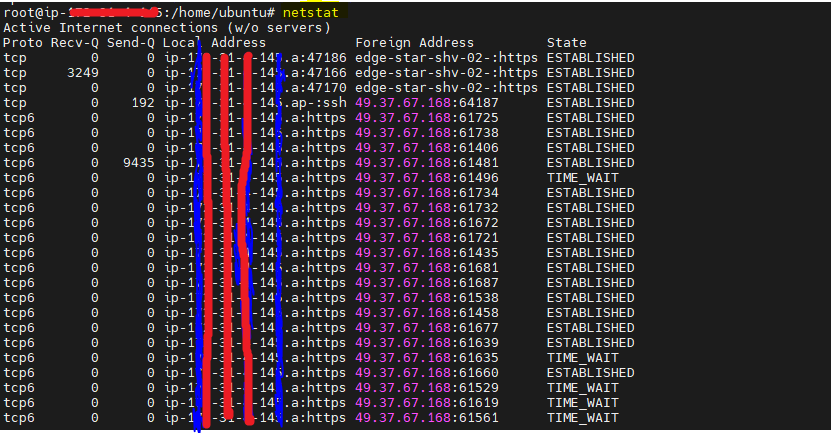
netstat: Display network connections, routing tables, and interface statistics
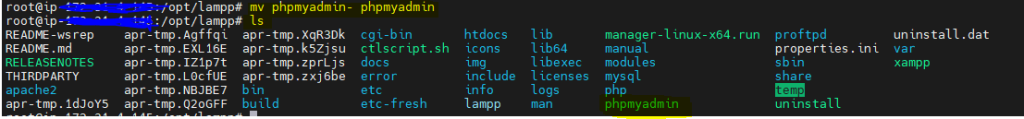
mv: Move or rename files or directories
Before:
After:
pwd: Print the name of the current directory

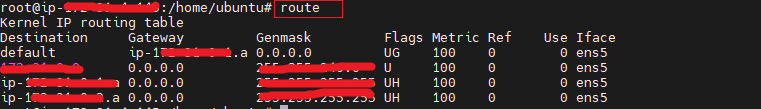
route: View and manipulate the IP routing table
iptables: Configure firewall rules
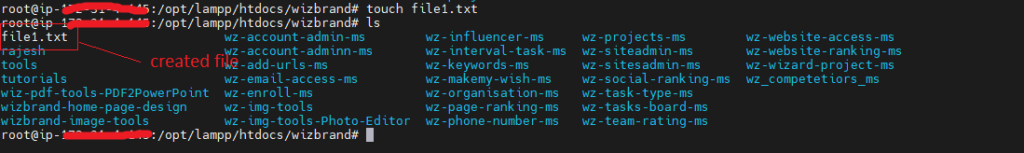
touch: create a new empty file
history: Display command history

For more information:-
How to Change the Permissions of Files and Directories in Ubuntu?
What is chmod command in Linux ?
How to Check Project Size in Linux
Hopefully, This blog will help you …!!!