
In this tutorial, you will learn about different operators available in JavaScript and how to use them with the help of examples.
What is an Operator?
An operator in JavaScript, is a symbol that is used to perform any assigned particular operation to operands (values and variables). For example,
let x = 10;
let y = 20;
document.write(x + y);
output:-
30
Here + is an operator that performs addition, and x and y are operands.
JavaScript Operator Types
Here is a list of different operators you will learn in this tutorial.
- Assignment Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- String Operators
- Other Operators
JavaScript Assignment Operators
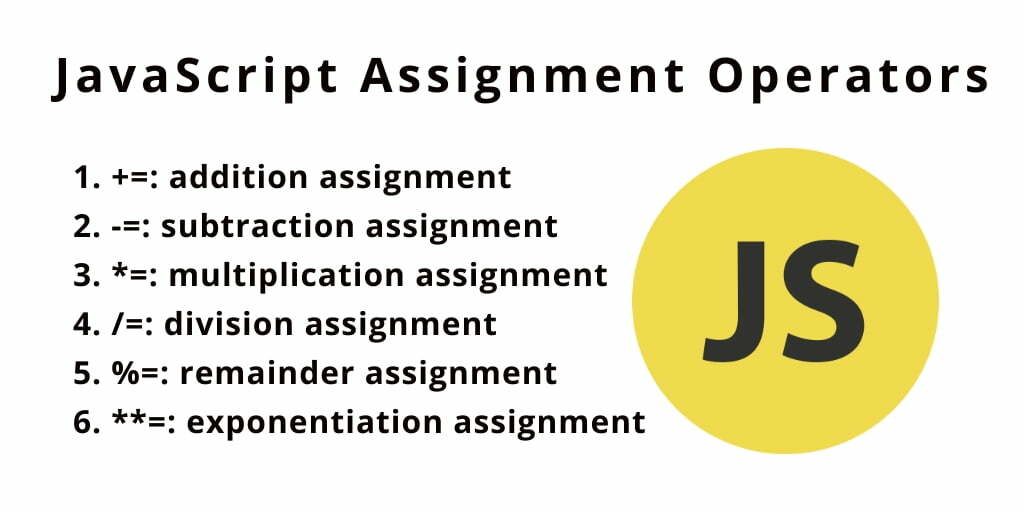
Assignment operators are used to assign any particular values to variables. For example,
let x = 10;
Here, the = operator is used to assign value 5 to variable x.
Here’s a list of commonly used assignment operators:
| Operator | Name | Example |
| “=” | Assignment operator | a = 7; // 7 |
| “=+” | Addition assignment | a += 5; // a = a + 5 |
| “-+” | Subtraction Assignment | a -= 2; // a = a – 2 |
| “*=” | Multiplication Assignment | a *= 3; // a = a * 3 |
| “/=” | Division Assignment | a /= 2; // a = a / 2 |
| “%=” | Remainder Assignment | a %= 2; // a = a % 2 |
| “**=” | Exponentiation Assignment |
JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
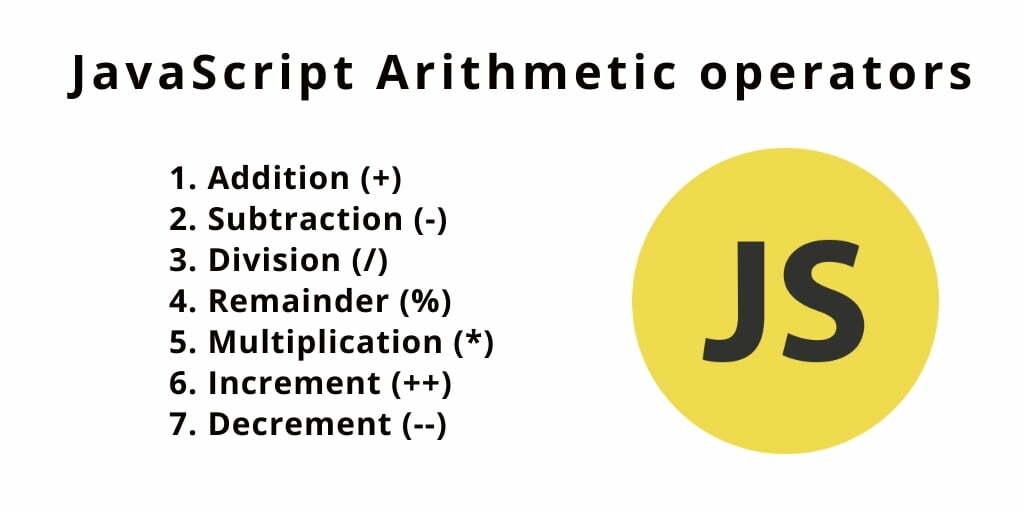
Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic calculations. For example,
const number = 10 + 20; // 30
Here, the + operator is used to add two operands.
| Operator | Name | Example |
| “+“ | Addition | x + y |
| “–“ | Subtraction | x – y |
| “*“ | Multiplication | x * y |
| “/“ | Division | x / y |
| “%“ | Remainder | x % y |
| “++“ | Increment (increments by 1) | ++x or x++ |
| “—“ | Decrement (decrements by 1) | –x or x– |
| “**“ | Exponentiation (Power) | x ** y |
JavaScript Comparison Operators

Comparison operators compare two values and return a boolean value, either true or false. Comparison operators are used in decision-making and loops.
For example,
const a = 5, b = 4;
console.log(a > b); // true
Here, the comparison operator > is used to compare whether a is greater than b.
| Operator | Name | Example |
| “==“ | Equal to: returns true if the operands are equal | x == y |
| “!=“ | Not equal to: returns true if the operands are not equal | x != y |
| “===“ | Strict equal to: true if the operands are equal and of the same type | x === y |
| “!==“ | Strict not equal to: true if the operands are equal but of different type or not equal at all | x !== y |
| “>“ | Greater than: true if left operand is greater than the right operand | x > y |
| “>=“ | Greater than or equal to: true if left operand is greater than or equal to the right operand | x >= y |
| “<“ | Less than: true if the left operand is less than the right operand | x < y |
| “<=“ | Less than or equal to: true if the left operand is less than or equal to the right operand | x <= y |
Example of Comparision Operator
JavaScript Logical Operators
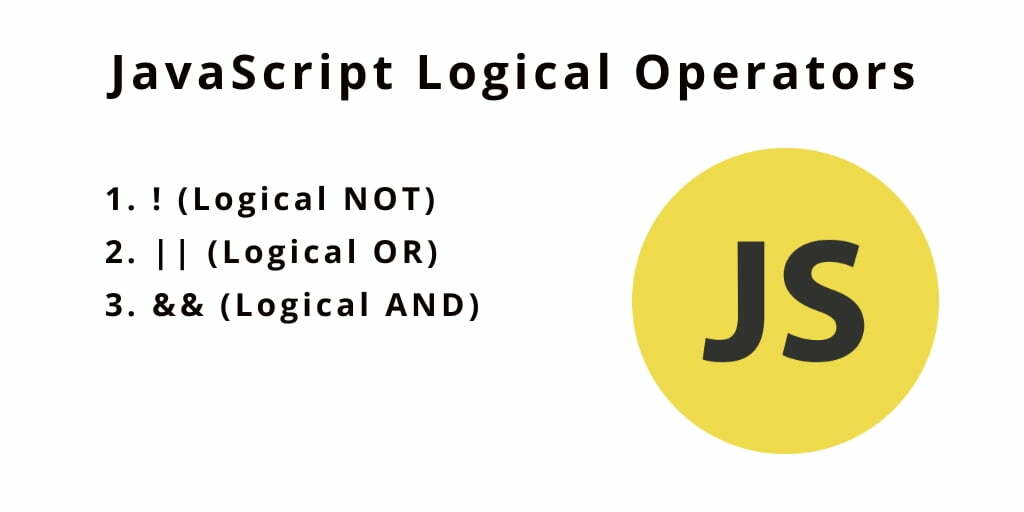
Logical operators perform logical operations and return a boolean value, either true or false.
Logical operators are used in decision making and loops.
For example,
const x = 8, y = 9;
(x < 10) && (y < 20); // true
Here, && is the logical operator AND. Since both x < 10 and y < 20 are true, the result is true.
| Operator | Description | Example |
| “&&“ | Logical AND: true if both the operands are true, else returns false | x && y |
| “||“ | Logical OR: true if either of the operands is true; returns false if both are false | x || y |
| “ ! “ | Logical NOT: true if the operand is false and vice-versa. | !x |
Example of Logical Operators in JavaScript
JavaScript String Operators
In JavaScript, you can also use the + operator to concatenate (join) two or more strings.
Example of String operators in JavaScript
Output:-
JavaScript is Awesome
Other JavaScript Operators
Here’s a list of other operators available in JavaScript. All this Operator is used as per requirment.
| Operator | Name | Example |
| “,“ | Evaluates multiple operands and returns the value of the last operand | let a = (1, 3 , 4); // 4 |
| “?:“ | Returns value based on the condition | (5 > 3) ? ‘success’ : ‘error’; // “success” |
| “delete“ | Deletes an object’s property, or an element of an array | delete x |
| “typeof“ | Returns a string indicating the data type | typeof 3; // “number” |
| “void“ | Discards the expression’s return value | void(x) |
| “in“ | Returns true if the specified property is in the object | prop in object |
| “instanceof“ | Returns true if the specified object is of of the specified object type | instanceof object_type |
Thats all for now, i hope you like this particular blog on JavaScript Opertors.
Thank You !!!